What Does Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Mean
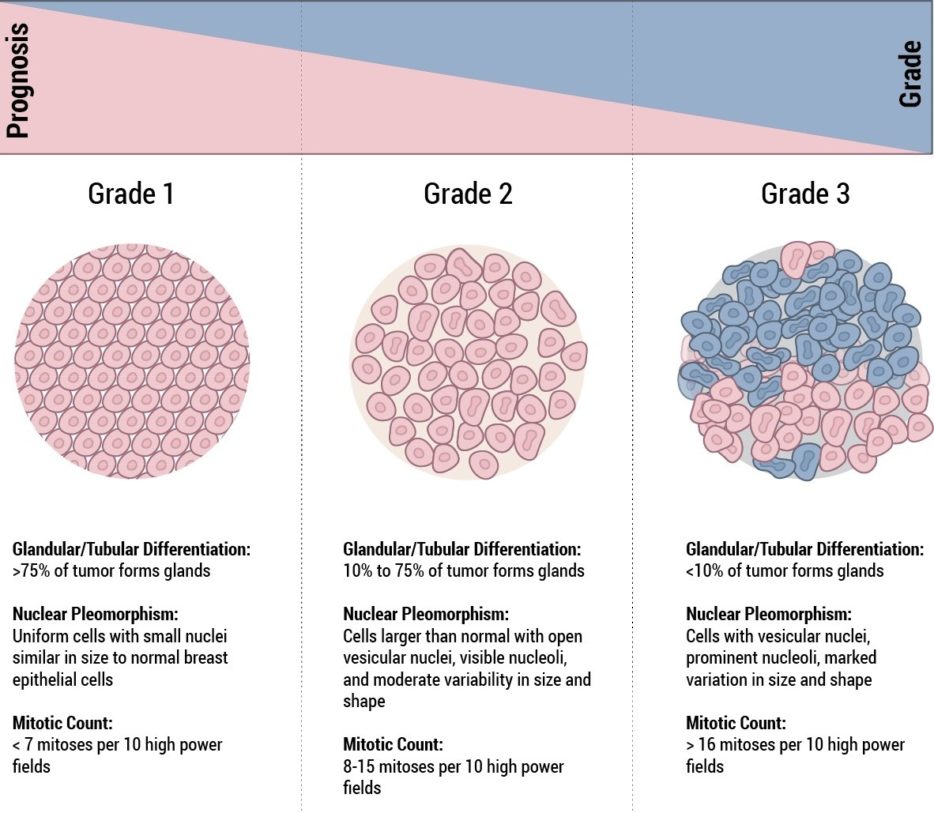
Grade 2 looks less like normal cells and is growing faster. IDC Invasive or Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma.
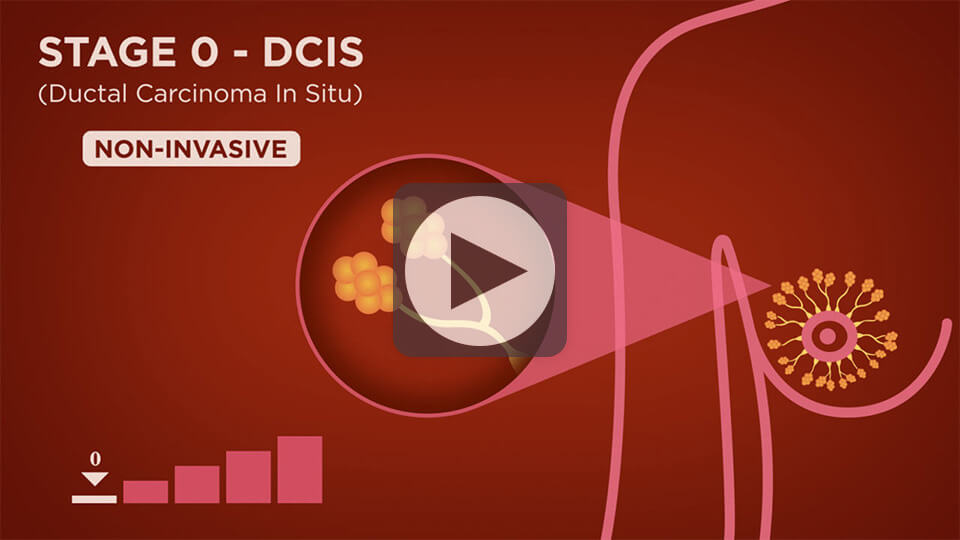
Stage 0 breast cancer ductal carcinoma in situ DCIS is a non-invasive cancer where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct.
What does invasive ductal carcinoma grade 1 mean. Stage 1 A breast tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters in diameter and the cancer has not spread beyond the breast. It is also sometimes called infiltrative ductal carcinoma. Grade 1 looks most like normal breast cells and is usually slow growing.
There are three grades of invasive breast cancer. Or nuclear grade 1 nuclear grade 2 or nuclear grade 3. Mucinous carcinoma of the breast sometimes called colloid carcinoma is a rare form of invasive ductal carcinoma cancer that begins in the milk duct and spreads beyond it into nearby healthy tissue.
All together invasive ductal carcinoma refers to cancer that has broken through the wall of the milk duct and begun to invade the tissues of the breast. Invasive ductal carcinoma is usually described through a numeric scale ranging from 1 the earliest stage to 4 the most advanced stage. Stage 2 A breast tumor measures 2 to 4 centimeters in diameter or cancerous cells have spread to the lymph nodes in the.
In this type of cancer the tumor is made up of abnormal cells that float in pools of mucin a key ingredient in the slimy slippery. Prognosis and Survival Rate. In the next image the malignant carcinoma has progressed to the extent that normal-appearing neoplastic tubules.
These are all different ways of describing how the DCIS looks under the microscope. IDC is the most common form of breast cancer representing 80 percent of all breast cancer diagnoses. With IDC cancer cells start in a milk duct break through the walls and invade breast tissue.
The abnormal cells start developing in the milk ducts then invades the surrounding tissue. This study compared mixed invasive ductal and lobular carcinoma IDC-L with invasive lobular carcinomas ILCs to assess the overall prognosis the prognostic role of histologic grade. In some cases the tumor can have features of both and are called mixed ductal and lobular carcinoma.
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma IDC is an invasive cancer where abnormal cancer cells that began forming in the milk ducts have spread beyond the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Specifically the invasive ductal carcinoma stages are. Once the cancer has metastasized to distant organs like the bones or liver the five-year survival rate drops by almost three fourths.
Ductal carcinoma can remain within the ducts as a noninvasive cancer ductal carcinoma in situ or it can break out of the ducts invasive ductal carcinoma. Lobular carcinoma starts in the lobules of the breast where breast milk is produced. In general there is not a significant different prognosis between invasive lobular and invasive ductal adenocarcinoma of the breast.
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment Listed below are the treatment modalities for invasive ductal carcinoma. If they add up to 6 or 7 it means the cancer is grade 2 moderately differentiated. This is the most common type making up about 80.
Invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body. Grade 3 looks different to normal breast cells and is usually fast growing. Invasive ductal carcinoma begins in the milk ducts of the breast and invades the surrounding breast tissue.
Invasive ductal carcinoma IDC also known as infiltrating ductal carcinoma is cancer that began growing in a milk duct and has invaded the fibrous or fatty tissue of the breast outside of the duct. What does it mean if my ductal carcinoma in situ DCIS is described as being low grade intermediate grade or high grade. Once it becomes invasive it spreads to the surrounding tissues.
Determining varations in the size and shape of malignant nuclei would require greater magnification. Grade 2- moderately differentiated or intermediate stage. A likely diagnosis would be grade I infiltrating ductal carcinoma.
Grade 1- well differentiated or low grade. The two major patterns seen in breast carcinoma are ductal carcinoma or lobular carcinoma. Histologic grade is an important prognostic factor in IDC-L but not in ILC.
Invasive ductal carcinoma IDC. Grade 3- poorly differentiated or high grade. Abnormal cells begin developing in the milk-producing tissues.
Invasive ductal carcinoma also called infiltrating ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast cancer accounting for about 80 of all cases of breast cancer. Systemic Chemotherapy generally used for malignant carcinoma. What Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma.
If the numbers add up to 3-5 the cancer is grade 1 well differentiated. Or low mitotic rate intermediate mitotic rate or high mitotic rate. ILC Invasive Lobular Carcinoma.
80 of all breast cancers are IDC making this the most common form of breast cancer. In Stage 0 breast cancer the atypical cells have not spread outside of the ducts or lobules into the surrounding breast tissue. Numbers are assigned to different features gland formation nuclear grade and mitotic count seen under the microscope and then added up to assign the grade.
When it breaks out of the lobules its considered invasive lobular carcinoma. Carcinoma refers to any cancer that begins in the skin or other tissues that cover internal organs such as breast tissue.

Pin By Koren Something On Pediatric Cancer Awareness Childhood Cancer Childhood Cancer Awareness Month Childhood Cancer Awareness
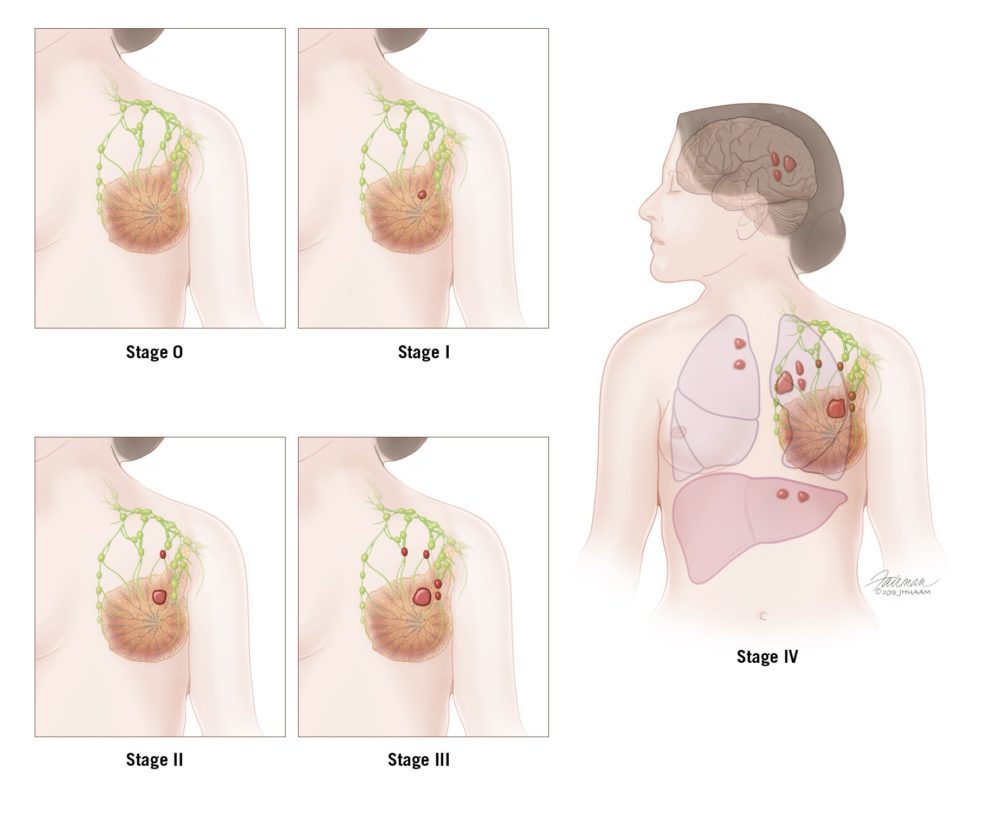
Staging Grade Breast Pathology Johns Hopkins Pathology

Stages 0 1 National Breast Cancer Foundation

Pin On Donna Jean Ford 4 16 60 2 14 09

Pin On Shirt Bags Pillow Ideas
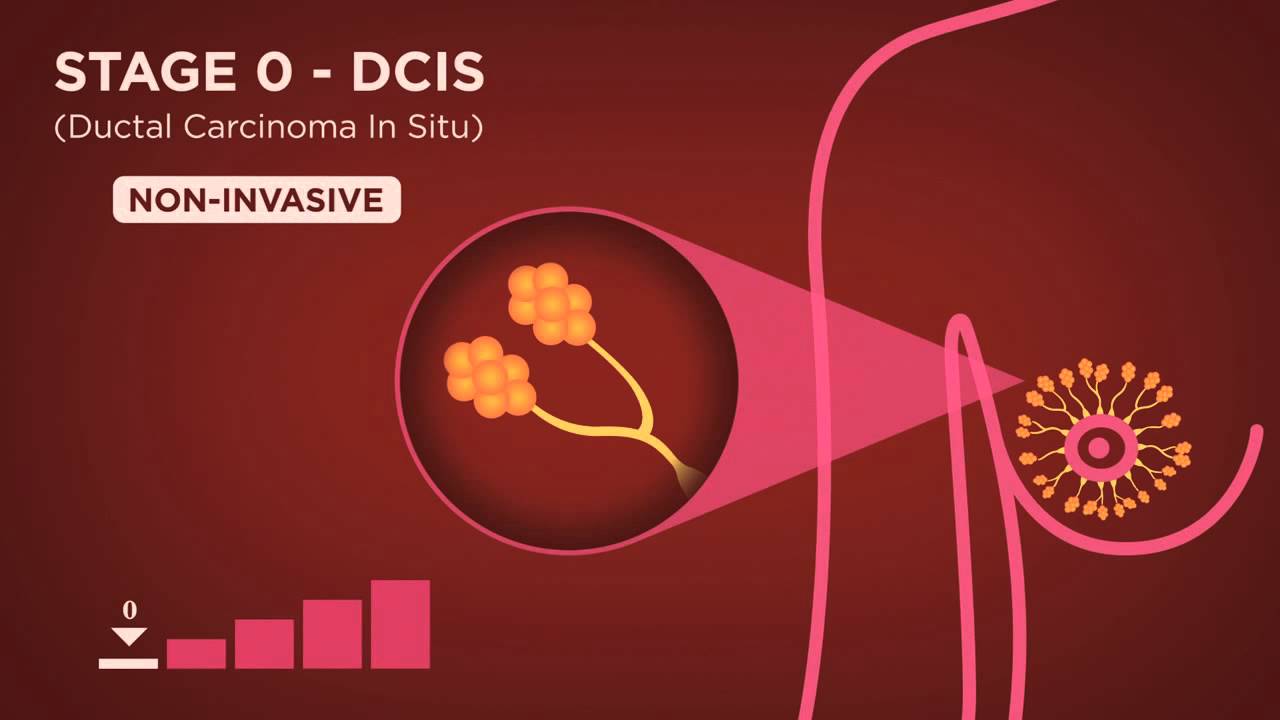
Stages 0 1 National Breast Cancer Foundation
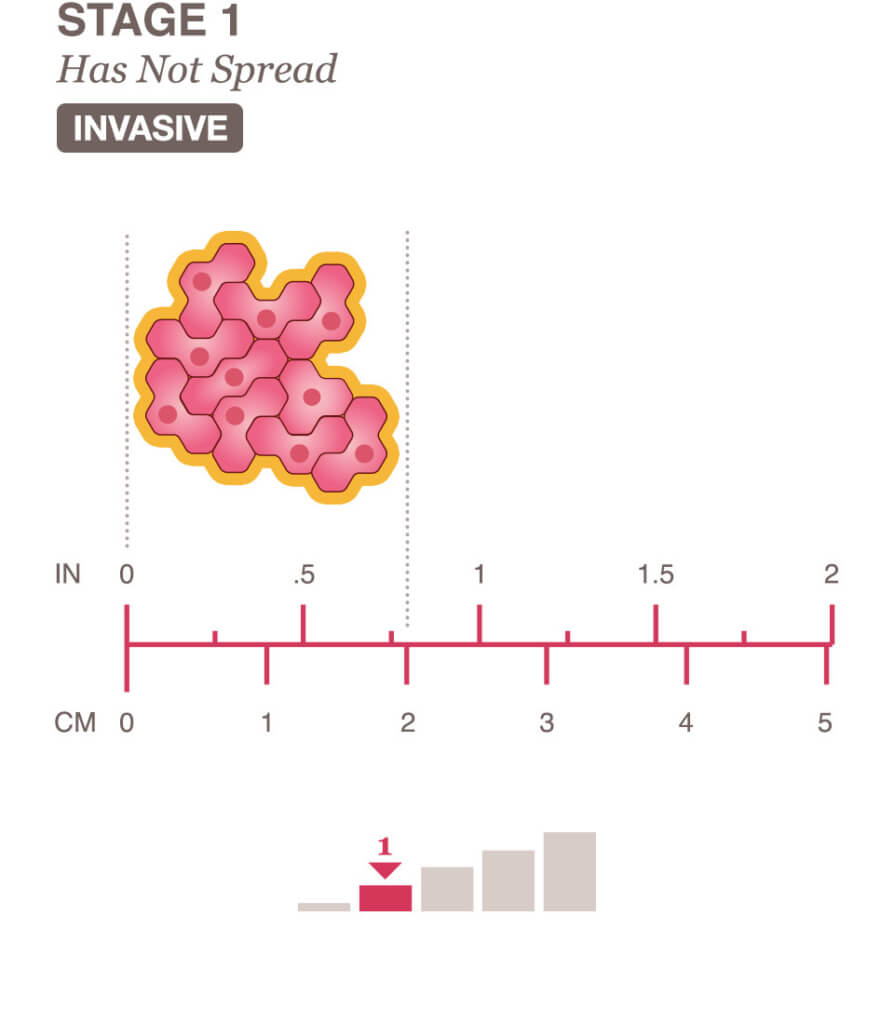
Stages 0 1 National Breast Cancer Foundation

Stage 1 Breast Cancer Cancer Research Uk

Breast Cancer Types And Stages Mybreastcancertreatment Org
Staging Grade Breast Pathology Johns Hopkins Pathology

Poetry I Love In 2021 Love Poems And Quotes Cancer Inspirational Quotes Compassion Poems

How Serious Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma

Pin On Words Make The Difference






